
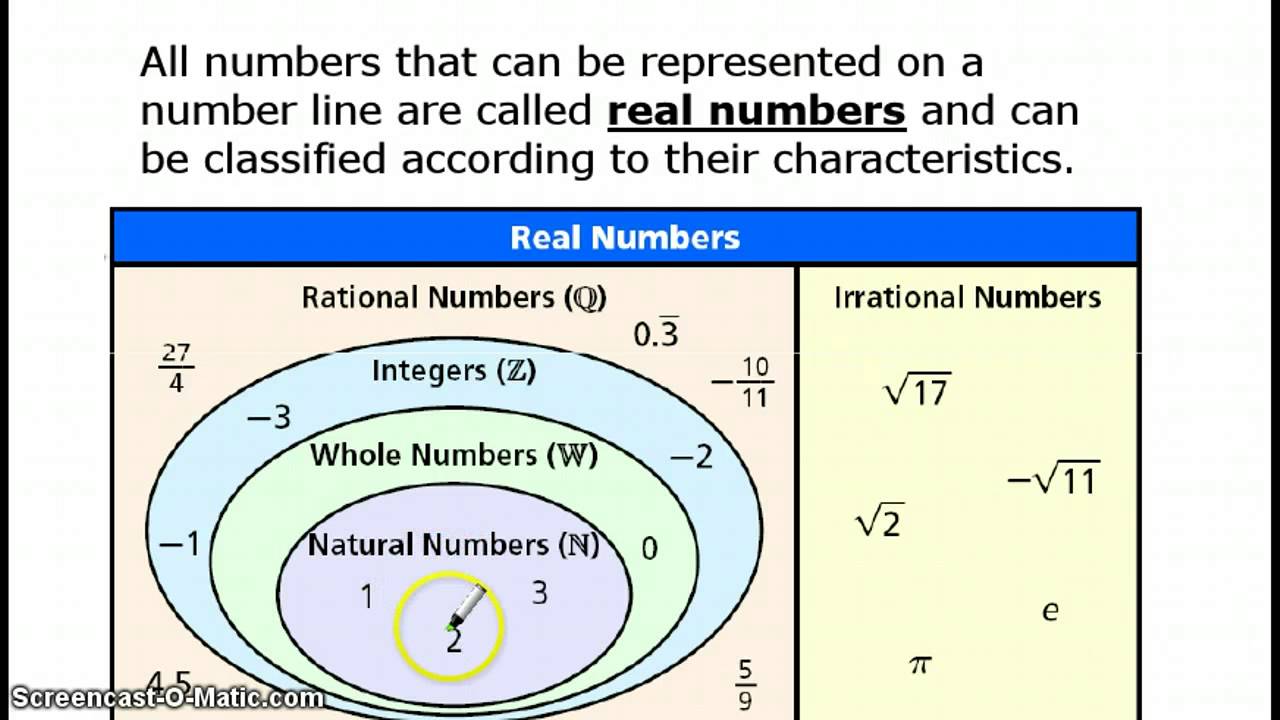
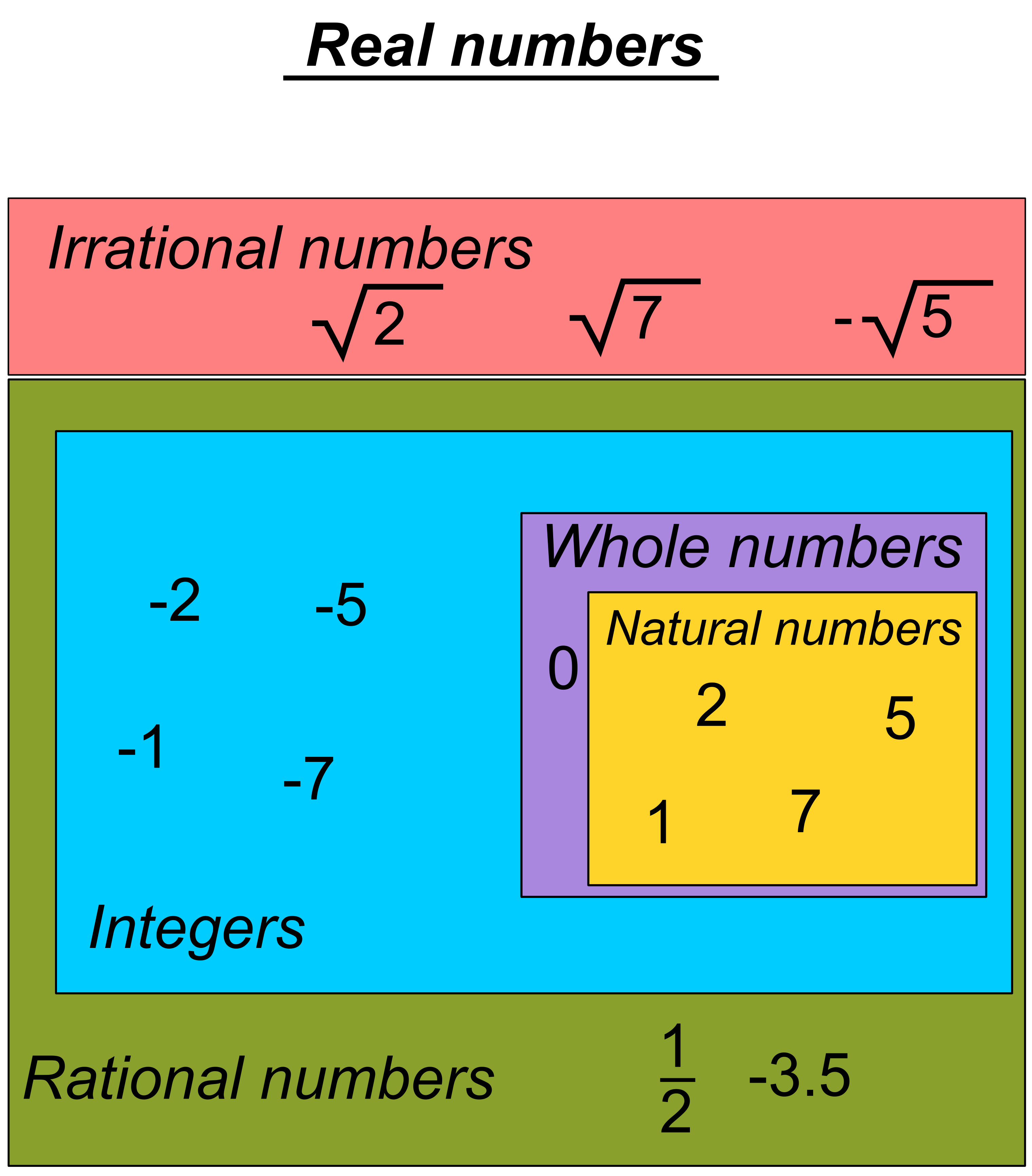
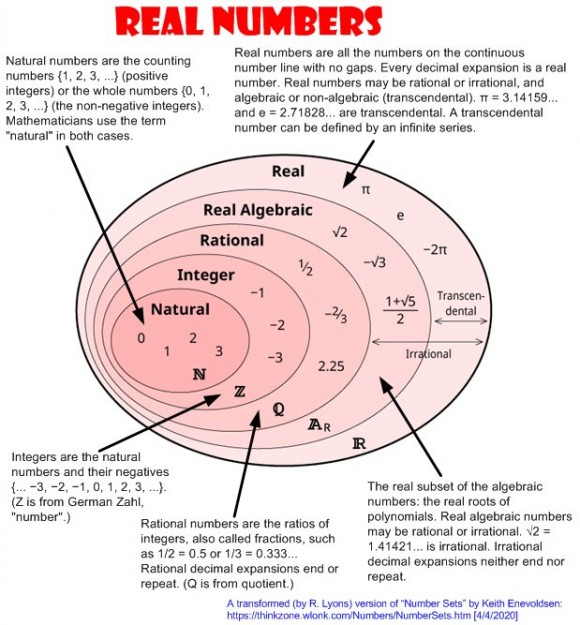
The set of the natural numbers (also known as counting numbers) contains the. ), where each term adds a digit of the decimal expansion of the positive square root of 2, is Cauchy but it does not converge to a rational number (in the real numbers, in contrast, it converges to the positive square root of 2). Five (5) Subsets of Real Numbers 1) The Set of Natural or Counting Numbers. The set of rational numbers is not complete. This definition, originally provided by Cauchy, formalizes the fact that the x n eventually come and remain arbitrarily close to each other.Ī sequence ( x n) converges to the limit x if its elements eventually come and remain arbitrarily close to x, that is, if for any ε > 0 there exists an integer N (possibly depending on ε) such that the distance | x n − x| is less than ε for n greater than N.Įvery convergent sequence is a Cauchy sequence, and the converse is true for real numbers, and this means that the topological space of the real numbers is complete. More formally, the reals are complete (in the sense of metric spaces or uniform spaces, which is a different sense than the Dedekind completeness of the order in the previous section):Ī sequence ( x n) of real numbers is called a Cauchy sequence if for any ε > 0 there exists an integer N (possibly depending on ε) such that the distance | x n − x m| is less than ε for all n and m that are both greater than N. Main article: Completeness of the real numbersĪ main reason for using real numbers is so that many sequences have limits. The set of real numbers is denoted R or R Topological completeness The real numbers are fundamental in calculus (and more generally in all mathematics), in particular by their role in the classical definitions of limits, continuity and derivatives. Every real number can be almost uniquely represented by an infinite decimal expansion. Here, continuous means that pairs of values can have arbitrarily small differences. Points to the right are positive, and points to the left are.
A point is chosen on the line to be the origin. In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a continuous one- dimensional quantity such as a distance, duration or temperature. The Real Number Line is like a geometric line. Columbia University.For the real numbers used in descriptive set theory, see Baire space (set theory). “Private tutoring and its impact on students' academic achievement, formal schooling, and educational inequality in Korea.” Unpublished doctoral thesis. In short, the set formed by the negative integers, the number zero and the positive integers (or natural numbers) is called the set of integers.
ARE ALL NUMBERS REAL NUMBERS PROFESSIONAL
Tutors, instructors, experts, educators, and other professionals on the platform are independent contractors, who use their own styles, methods, and materials and create their own lesson plans based upon their experience, professional judgment, and the learners with whom they engage. Varsity Tutors connects learners with a variety of experts and professionals. Varsity Tutors does not have affiliation with universities mentioned on its website. Media outlet trademarks are owned by the respective media outlets and are not affiliated with Varsity Tutors.Īward-Winning claim based on CBS Local and Houston Press awards.
ARE ALL NUMBERS REAL NUMBERS PLUS
Names of standardized tests are owned by the trademark holders and are not affiliated with Varsity Tutors LLC.Ĥ.9/5.0 Satisfaction Rating based upon cumulative historical session ratings through 12/31/20. all of the counting numbers (1, 2, 3, etc.) plus 0 Integers: (can be positive or negative) all of the whole numbers (1, 2, 3, etc.) plus all of their opposites (-1, -2, -3, etc.) and also 0 Rational numbers: any number that can be expressed as a fraction of two integers (like 92, -56/3, 25, or any other number with a repeating or terminating. Hamilton in 1845, form a number system with three Is important because for any polynomial p ( x ) with real number coefficients, all the solutions of p ( x ) = 0 will be in C. The real numbers, in the complex system, are written in the form a + 0 i = a. The complex numbers include the set of real numbers. When the precision of a FLOAT is in the range of 1 to 21, the query processor treats the. More on imaginary numbers and operations with complex numbers). Single precision floating-point (REAL or FLOAT) A single-precision, floating-point number is a 32-bit approximation of a real number. The set of natural numbers,, where i is the imaginary unit, − 1. The natural (or counting) numbers are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, etc. Number Systems: Naturals, Integers, Rationals, Irrationals, Reals,


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
